Two years ago, we decided to aim Katakri approval. The process started by working on existing safety guidelines in the required form. A closer look at Katakri showed that the company’s operating methods and guidelines for security had been implemented at the level of requirements already for years. The process was completed in October when the competent authority audited Ontec Oy’s premises, operating methods, and electronic data processing equipment. We passed the audit and are now Katakri qualified company.
The Katakri 2020 audit has strengthened our idea of where we are going and what we demand for the development of our own operations in the future. Now it is time to move on from this to new challenges.
What is Katakri?
Katakri is an information security audit tool for authorities. It can be used as an audit tool for a Facility Security Clearance (FSC) to assess how a company’s security arrangements are implemented and to assess the authorities information assurance.
Facility Security Clearance, FSC
In the Facility Security Clearance procedure, the competent authority asses how the company is able to take care of given security responsibilities. This is achieved through the use of information sources listed in the Act, through vetting’s of personnel and through audits of security management and premises of the company.
Security audits includes, for example, safeguarding procedure of Classified Information from untrue disclosure, preventing untrue access to premises where classified information is processed and stored, and instructing and training company personnel (Figure 2).
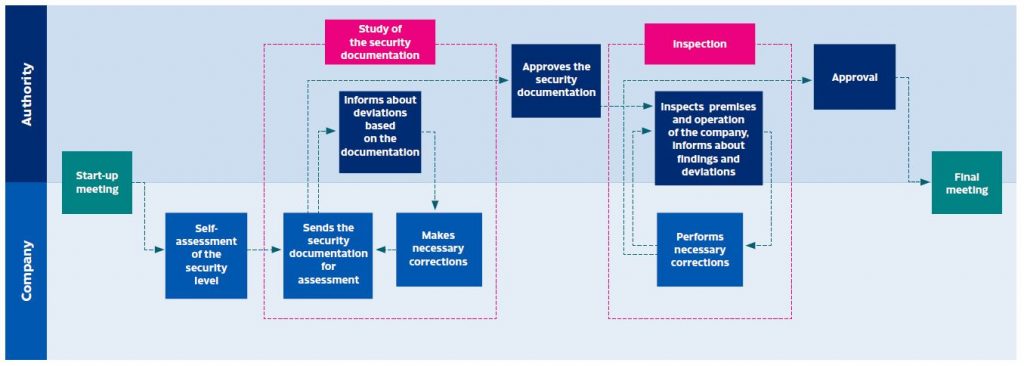
The assessment of sufficient security arrangements made in the company must be based on a systematic risk assessment. The management of these risks will create satisfactory balance among user requirements, costs and residual safety risk.
History of Katakri
Katakri’s first version was finished in 2009 as part of the government’s internal security program. Since then, the responsibility of Katakri’s maintenance and administration has been led by the steering group working under the NSA (Nation Security Authority). The steering group consists representatives from different authors like ministries and industry. There is currently a fourth version of Katakri, the latest pays special attention to the development steps of the digital data processing.
Katakri includes minimum standards based on national regulations and international obligations. At national level, the most important pieces of legislation in the context of Katakri are the Act on Information Management in Public Administration (906/2019) and the Government Decree on Security Classification of Documents in Central Government (1101/2019). Katakri’s requirements have been divided into three subdivisions: Security Management, Physical Security, and Information Assurance.


